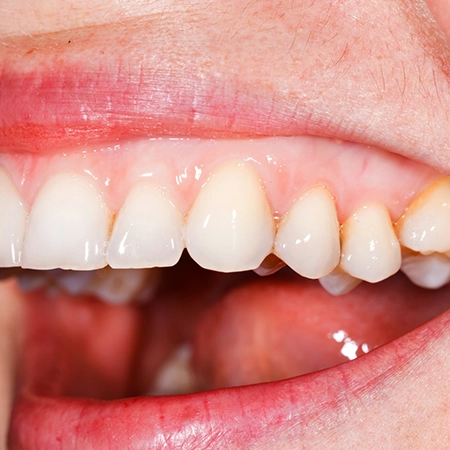
Leukoplakia is a condition characterized by thickened, white patches that can develop on the mucous membranes of the mouth and sometimes on the tongue. These patches are usually painless, but they can be precancerous, meaning they have the potential to develop into oral cancer. It's essential for anyone with leukoplakia to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and management. White gums can indicate a variety of underlying issues. Some of the most common causes of white gums includes: It's crucial to consult with a dentist or healthcare professional if you notice any unusual changes in your gum color for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The symptoms associated with white gums can vary depending on the underlying cause, but some common signs may include: If you notice any of these symptoms, it's essential to seek advice from a healthcare professional or dentist for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Regular dental check-ups can also help detect potential issues early on. The treatment for white gums depends on the underlying cause of the discoloration. Here are some common treatments associated with specific causes: It's important to consult with a healthcare professional or dentist to determine the specific cause of white gums and tailor the treatment accordingly. Early detection and appropriate management are key to addressing underlying issues and preventing potential complications. If you have any questions or concerns about your white gums, your dental professional can help. They have the training and expertise to help you understand your condition and the best ways to address it. Below are a few of the most commonly asked questions: The time it takes for white gums to return to normal can vary widely depending on the underlying cause. Improvements may be seen within a few days to weeks with appropriate treatment, but it's essential to follow the advice of a healthcare professional for a more accurate estimate. Injured gums may not necessarily turn white. Instead, they might become red, swollen, or bleed. White discoloration is more commonly associated with other conditions like leukoplakia, oral thrush, or lichen planus. Healthy gums are typically pink or coral in color. The specific shade can vary among individuals, but a normal gum color is generally a lighter pink compared to the surrounding oral tissues. Gums should also have a firm texture and not exhibit signs of inflammation, such as redness, swelling, or white patches. Regular dental check-ups can help ensure the health of your gums.What Causes White Gums?
What are the Common Symptoms of White Gums?
How are White Gums Treated?
Frequently Asked Questions about White Gums
How long does it take for white gums to return to normal?
Do injured gums turn white?
What color should your gums be?